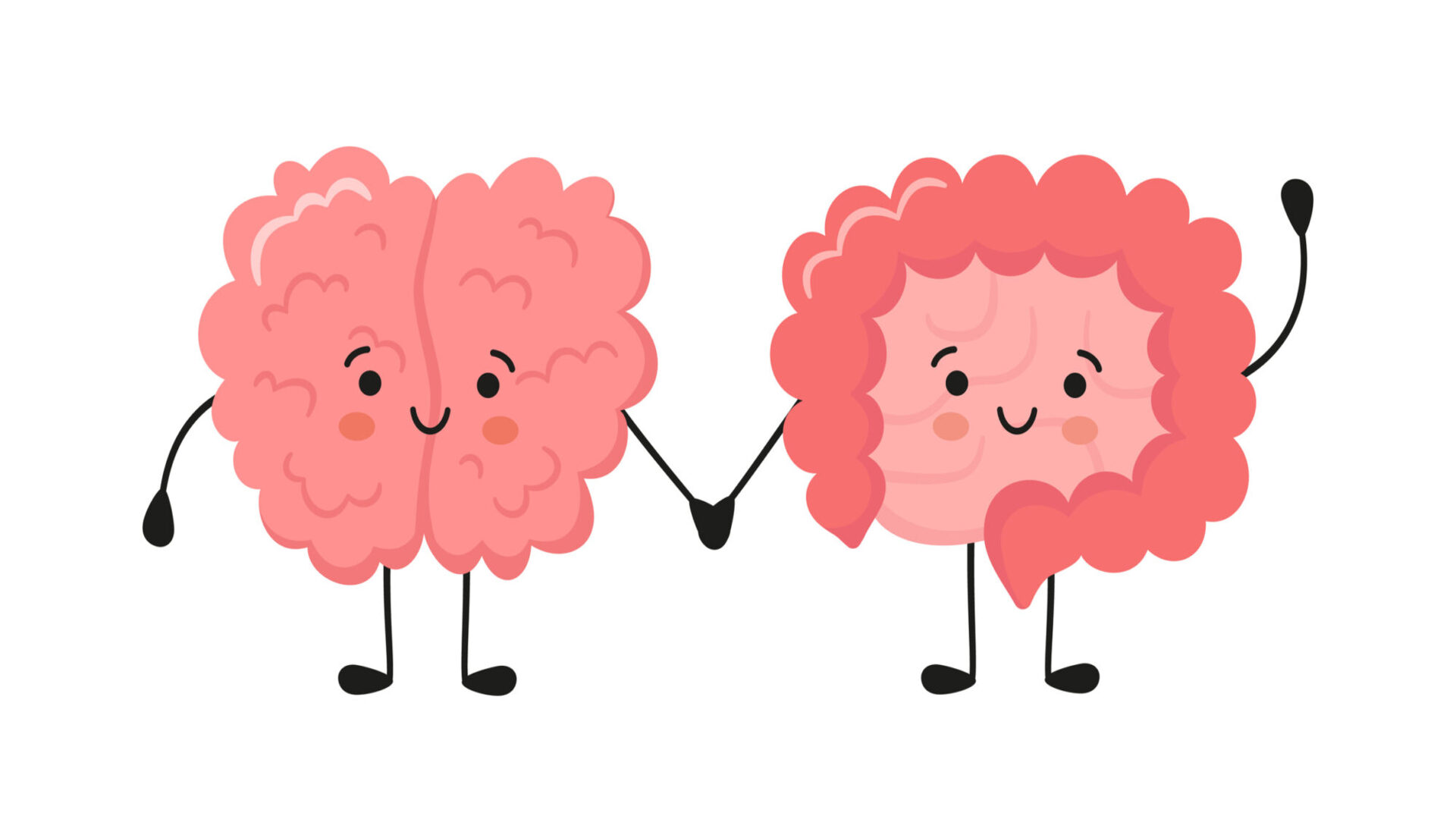
In recent years, research has increasingly highlighted the strong connection between gut health and mental health. The gut, or the so-called “second brain,” directly impacts mood, stress, and cognitive function. The gut-brain axis, a complex communication network between the digestive system and the central nervous system, plays a key role in this connection. This link promises to open up new avenues for treating mental health. It also holds potential for improving overall health.
The Gut-Brain Axis: How It Works
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system that links the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems. Some of the key players in this interaction include:
- The Vagus Nerve – A large nerve that sends messages from the gut to the brain and from the brain to the gut. It influences emotions and stress responses.
- Gut Microbiota – The trillions of bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract play a vital role. They help synthesize neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, which regulate mood and anxiety levels.
- Inflammation and Immunity – An imbalance or dysbiosis in the gut bacteria can trigger chronic inflammation. This inflammation links to depression and anxiety disorders.
- Nutrient Absorption – A healthy gut ensures it absorbs essential nutrients like B vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids, and amino acids. These nutrients support brain function and mental clarity.
How Gut Health Affects Mental Health
Research suggests that a weakened gut can cause various mental health issues, such as:
- Depression and Anxiety – Disruptions in gut microbiota composition have linked to elevated stress hormone levels. They also reduce serotonin production.
- Cognitive Decline – Poor gut health may contribute to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. This happens by increasing inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Stress and Mood Disorders – Gut microbiome imbalances may worsen stress responses. They make individuals more vulnerable to mood swings and irritability.
Ways to Improve Gut and Mental Health
Optimizing gut health can profoundly impact mental health. Here are some tips:
- Consume Probiotic-Rich Foods – Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi help maintain a balance of gut bacteria.
- Increase Prebiotics – Bananas, garlic, onions, and asparagus nourish beneficial bacteria.
- Consume a Diverse Range of Fiber-Rich Foods – Whole grains, legumes, and vegetables diversify the gut microbiome. This reduces inflammation.
- Avoid Processed Foods and Sugar – Excessive sugar and artificial substances harm gut bacteria. They worsen mental illness.
- Manage Stress – Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing help balance the gut-brain axis.
- Get Enough Sleep – Insomnia negatively affects gut bacteria. It also increases the risk of depression and anxiety.
- Exercise Regularly – Regular exercise improves gut health. It also boosts mood by releasing endorphins.
Conclusion
The gut and brain are closely interconnected. They influence each other through various biological processes. A healthy gut microbiome, supported by a balanced diet, stress management, and lifestyle changes, plays a significant role in promoting mental health. As research continues to explore this relationship, adopting gut-friendly habits into daily life may become a powerful strategy for enhancing overall well-being.
Share your own article on Aumet Blog
To learn more about Aumet, contact us!