3,954 Views
Drug discovery and development is known as the process of identifying a potential therapeutic agent to the approval of a new therapeutic agent by the FDA. This process plays a crucial role in advancing medicine, improving public health, and improving the overall quality of life. The continuous research of innovative therapies through this process ensures that healthcare remains at the forefront of scientific advancements, offering hope and improved outcomes for patients around the world.
Drug discovery and development importance:
- Economic Impact and Job Creation: the pharmaceutical sector is known for its economic contribution through creating jobs and production of new drugs.
- Disease Treatment: drugs manufactured from this process is used to: provide healthcare professionals with valuable tools to alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and enhance overall patient well-being.
- Global Health Security: the drug discovery and development process are crucial to effectively respond to global pandemics such as coronavirus.
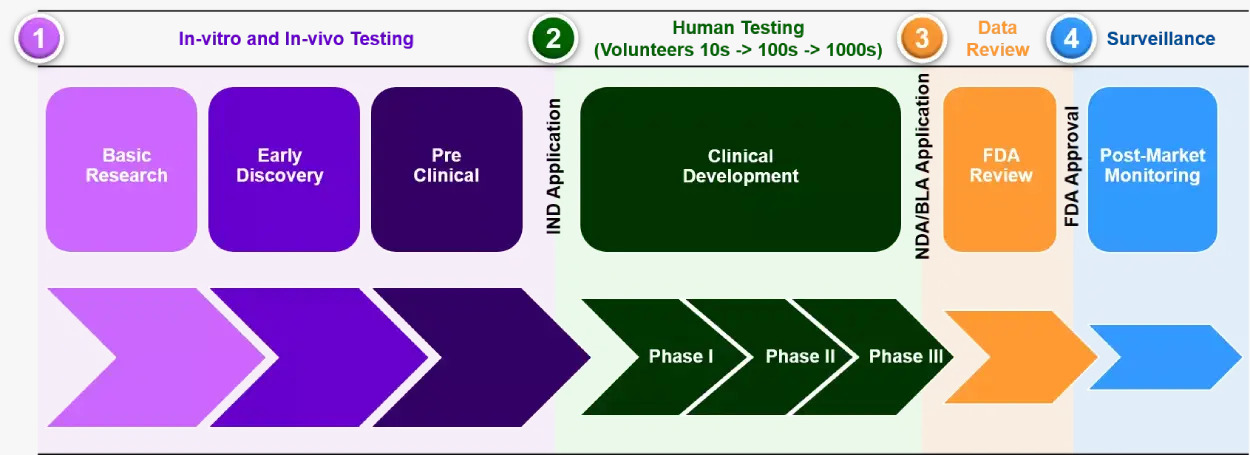
Drug discovery and development steps:
- Target Identification and Validation: This step involves identifying and validating a biological target such as protein, enzyme, and gene. Moreover, this step involves studying the molecular pathways associated with the disease.
- High-throughput Screening: After the identification of a target, thousands of chemical compounds are tested for their ability to interact with the selected target. Automated robotic systems play a crucial role in this process, rapidly screening compounds against the selected target to identify potential drug candidates (hits).
- Hit to Lead Optimization: Only few compounds exhibit potential therapeutic effects after the screening. Then, these compounds (Hits) undergo a process called lead optimization, where efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetic properties are enhanced.
- Preclinical trial: Once a lead compound is successful, preclinical studies will be conducted to assess its safety and activity. This stage involves testing in cell cultures and animal models to evaluate the drug’s biological activity, potential toxicity, and overall safety. This step provides information whether the drug candidate should proceed to clinical trials or not.
- Clinical Trials: In this phase, human subjects are used to test the drug safety and efficacy. This phase is divided into 3 stages: Phases I, phase II, and phase III. Each phase provides information about the safety, dosage, and effectiveness of the drug.
- Regulatory Approval: after clinical trials, new drug application is formed and submitted into regulatory authorities such as Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This step is to ensure the drug’s safety, efficacy, and quality before granting approval for market release.